APPENDIX A
Database Description
WebMILS is a database system designed toprovide convenient access to all available data indicators that relate to compliance with international labor standards. This database was designed for the U.S. Department of Labor by the Committee on Monitoring International Labor Standards during 2001-2003.
The database structure consists of a data cell for every combination of variable and political jurisdiction. To illustrate how to populate the data cells, the committee has populated the structure for a single country: South Africa. It remains for others to populate the database for all the political jurisdictions.
INTERNATIONAL LABOR STANDARDS COVERED
WebMILS provides information on the four international labor standards included in the 1998 International Labour Organization’s Declaration of Fundamental Principles and Rights at Work:
-
freedom of association and the effective recognition of the right to collective bargaining;
-
the elimination of all forms of forced or compulsory labor;
-
the effective abolition of child labor; and
-
the elimination of discrimination in respect of employment and occupation.
In addition, in accordance with the U.S. trade law, information is provided on a fifth standard:
-
acceptable conditions of work with respect to minimum wages, hours of work, and occupational safety and health.
INDICATORS DEVELOPED
For each of these standards, the committee organized its indicators into three domains: (1) legal framework, (2) government performance, and (3) overall outcomes. A fourth domain (4) covers relevant, associated factors. Within these four domains, indicators are grouped in terms of the five primary categories:
-
freedom of association and collective bargaining,
-
forced labor,
-
child labor,
-
discrimination and equality, and
-
acceptable conditions of work.
In addition, a sixth category concerns measures of human capital.
To a large extent, the committee sought to create a list of indicators that should be included, regardless of whether information on them is currently being collected. WebMILS will contain data on these indicators, which are relevant to an assessment of compliance or noncompliance with each of the five labor standards.
Many indicators are operational and data or information is currently being collected; such indicators are included in the database. For several indicators, the indicators are operational, but no data or information is currently collected; these indicators are presented with the hope that data will be available in the future. Users may notice that the same indicator appears for multiple standards. The committee’s view is that a country’s compliance should be judged against each standard and that some indicators are relevant for more than one standard.
POLITICAL JURISDICTIONS
The database structure is designed to allow for an examination of many political entities. Examples of political entities are independent nation-states and territories and special dependencies (e.g., as listed in the annual CIA World Factbook). Over time, more and more entities and more and more data can be added to the database.
MAIN COMPONENT: THE COUNTRY PAGE
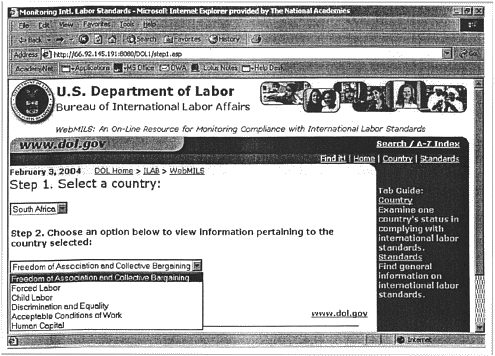
After entering WebMILS through the Home page (see Figure A-1), assessors may access data through the Country page. Using the drop down menus on the Country page, assessors may select a country of interest and then one of the five labor standards or human capital (see Figure A-2). These two selections are linked to further information on that topic, directing the user to a brief discussion by the committee on the topic that has been selected (see Figure A-3). By following the link at the bottom of the page, assessors are directed to a list of indicators (or measures in the case of human capital). From this list, (see Figure A-4), the user can select an individual variable. Doing so will open a new page, (see Figure A-5) which contains information for that specific country and variable. This page always follows the same structure, and includes:
-
Definition: this is the definition of the variable.
-
Assessment/discussion of indicator: here, the committee discusses the nature of the indicator, how it might be interpreted, issues, complexities, etc.
-
Information: the committee presents any information on that variable.
-
Available Sources: the committee presents a list of potential sources of information on the indicator, for this country. (Additional sources may be added later by those who are charged with maintaining the database.) For most sources, the committee identifies a link to the available data (e.g., a link to a particular agency and report, such as an ILO publication) and a link to the committee’s own assessment of the source of information (see Figure A-6).
-
Further information: a place for further information. Again, additional sources may be added later and a feedback option is included for users to suggest further resources.
THE STANDARDS PAGE
The Standards page (see Figure A-7) presents two types of information. Links to the full text of the eight ILO core conventions are provided here. Second, there are links to other websites of interest (either generally on the international labor standards—e.g., to the International Labour Organization—or specifically on a particular standard—e.g., the International Confederation of Free Trade Unions).