SLIDE 2

SLIDE 2 NOTES: The CISNET initiative has some features that are closely aligned to the purposes of this workshop but many features in addition. It is an NCI-sponsored consortium focused on the “Why?” and “What if?” questions in cancer trends. So, it goes beyond the issues of cost-effectiveness modeling to the modeling of population trends.
CISNET is intended to further statistical modeling of the impact of cancer, taking into account the impact of the full range of cancer control interventions-prevention, screening and treatment—on current and future trends.
We have had two rounds of funding so far. These have been four-year grants by the National Cancer Institute (NCI). They are U01 cooperative agreements, which means that the staff at NCI work in cooperation with the grantees. In 2000, we began with three cancer sites—breast, prostate and colorectal cancer-and funded 9 grants. Most of those grants were in the area of breast cancer, reflecting the state of modeling at the time. Eight more grants were funded in 2002, and lung cancer was added to the list of sites
SLIDE 3
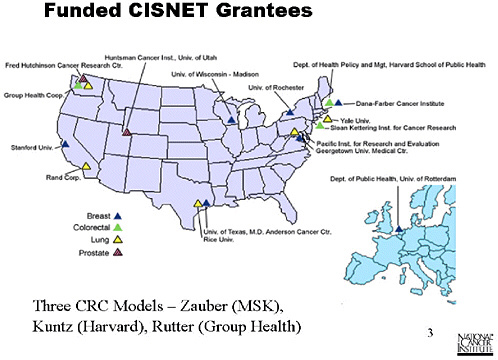
SLIDE 3 NOTES: The modelers in CISNET represent a well respected and diverse group of cancer modelers.
The MISCAN group from the Netherlands was one of the first groups in the world to do modeling of this type. Besides having a breast grant of their own, their colorectal model is being used by the funded group at Memorial Sloan Kettering, and the lung model being developed at Rand is a transplanted MISCAN person.
SLIDE 6

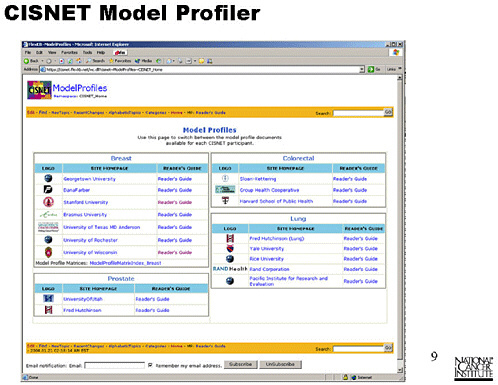
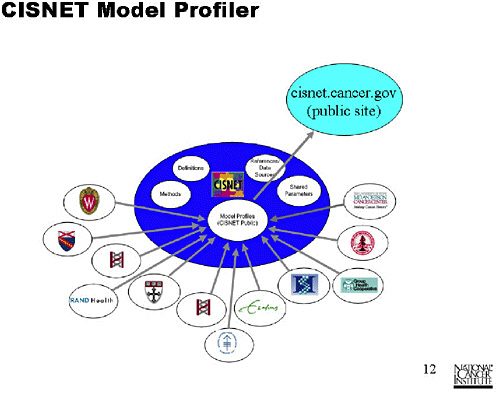
SLIDE 6 NOTES: This workshop grew out of one of the same issues that CISNET has had to address: the lack of comparability of inputs, outputs, structures and definitions among different models of the same cancer site.
We have tried to address this problem in CISNET with tools called “Model Profiler,” and “Base Cases.” I will discuss both of these efforts.
SLIDE 8
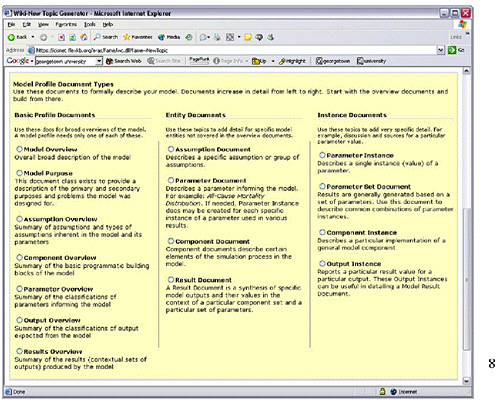
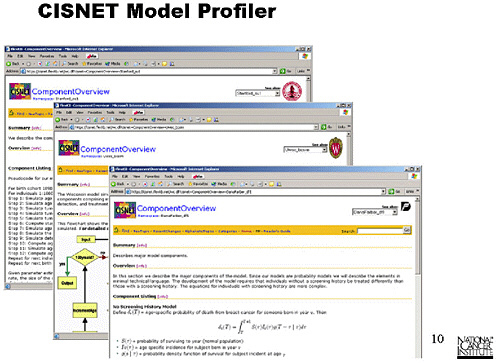
SLIDE 8 NOTES: Here is the structured format for entry of documentation into Model Profiler. There are a number of basic profile documents, a model overview, a model purpose, and an assumption overview. Ideally, all collaborators would enter information into each of these documents.
It is possible to go deeper and enter documents that address specific assumptions or parameters. Although we are encouraging groups to use this profiler, they are free to go into as much depth as they want to.
SLIDE 13
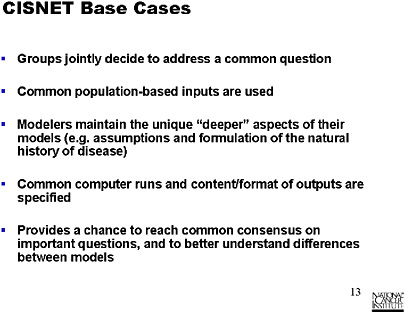
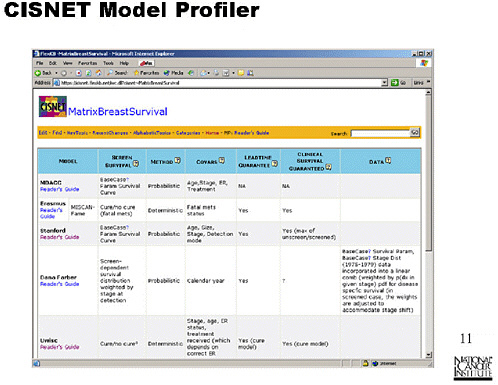
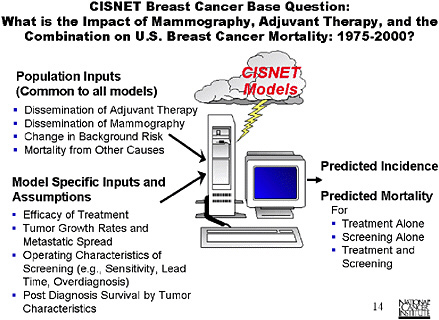
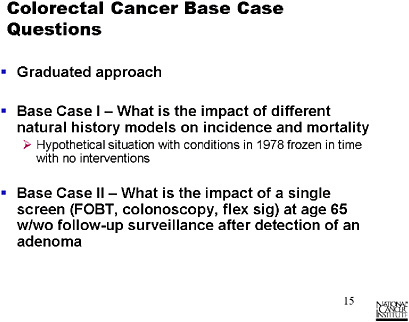
SLIDE 13 NOTES: The CISNET Base Cases initiative is similar to what the modelers at this workshop have been attempting to do. The group jointly decides to address a common question. We have common population-based inputs, and the modelers maintain what I would call the deeper aspects of their models, e.g., assumption and formulation of natural histories.
We produce a set of common computer runs, and the format of the outputs is specified. That provides a chance to reach a consensus on important questions and to better understand differences among the models.