5
The Role of Nurses in Improving Health Equity
Being a nurse … in 2020 must mean being aware of social injustices and the systemic racism that exist in much of nursing … and having a personal and professional responsibility to challenge and help end them.
—Calvin Moorley, RN, and colleagues, “Dismantling Structural Racism:
Nursing Must Not Be Caught on the Wrong Side of History”
When this study was envisioned in 2019, it was clear that the future of nursing would look different by 2030; however, no one could predict how rapidly and dramatically circumstances would shift before the end of 2020. Over the coming decade, the nursing profession will continue to be shaped by the pressing health, social, and ethical challenges facing the nation today. Having illuminated many
of the health and social inequities affecting communities across the nation, the COVID-19 pandemic, along with other health crises, such as the opioid epidemic (Abellanoza et al., 2018), presents an opportunity to take a critical look at the nursing profession, and society at large, and work collaboratively to enable all individuals to have a fair and just opportunity for health and well-being, reflecting the concept of “social mission” described by Mullan (2017, p. 122) as “making health not only better but fairer.” This chapter examines health equity and the role of nursing in its advancement in the United States.
As stated previously, health equity is defined as “the state in which everyone has the opportunity to attain full health potential and no one is disadvantaged from achieving this potential because of social position or any other socially defined circumstance” (NASEM, 2017a, p. 32). While access to equitable health care, discussed in Chapter 4, is an important part of achieving health equity, it is not sufficient. Health is affected by a wide range of other factors, including housing, transportation, nutrition, physical activity, education, income, laws and policies, and discrimination. Chapter 2 presents the Social Determinants of Health and Social Needs Model of Castrucci and Auerbach (2019), in which upstream factors represent the social determinants of health (SDOH) that affect individuals and communities in a broad and, today, inequitable way. Low educational status and opportunity, income disparities, discrimination, and social marginalization are examples of upstream factors that impede good health outcomes. Midstream factors comprise social needs, or the individual factors that may affect a person’s health, such as homelessness, food insecurity, and trauma. Finally, downstream factors include disease treatment and chronic disease management.
Much of the focus on the education and training of nurses and the public perception of their role is on the treatment and management of disease. This chapter shifts that focus to nurses’ role in addressing SDOH and social needs, including their potential future roles and responsibilities in this regard, and describes existing exemplars. First, the chapter provides a brief overview of nurses’ role in addressing health equity. Next, it describes opportunities for nurses to improve health equity through four approaches: addressing social needs in clinical settings, addressing social needs and SDOH in the community, working across disciplines and sectors to meet multiple needs, and advocating for policy change. The chapter then details the opportunities and barriers associated with each of these approaches.
NURSES’ ROLE IN ADDRESSING HEALTH EQUITY
As described in Chapter 1, the history of nursing is grounded in social justice and community health advocacy (Donley and Flaherty, 2002; Pittman, 2019; Rafferty, 2015; Tyson et al., 2018), and as noted in Chapter 2, the Code of Ethics for Nurses with Interpretive Statements, reiterated by American Nurses Association (ANA) President Ernest J. Grant in a public statement, “obligates nurses to be allies and to advocate and speak up against racism, discrimination, and injustice” (ANA, 2020).
Addressing social needs across the health system can improve health equity from the individual to the system level. The report Integrating Social Care into the Delivery of Health Care identifies activities in five complementary areas that can facilitate the integration of social care into health care: adjustment, assistance, alignment, advocacy, and awareness (NASEM, 2019) (see Figure 5-1 and Table 5-1). In
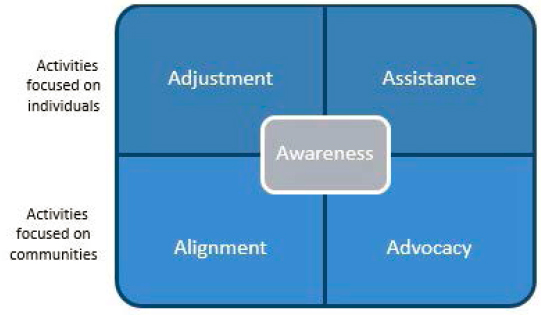
SOURCE: NASEM, 2019.
| Activity | Definition | Transportation-Related Example |
|---|---|---|
| Awareness | Activities that identify the social risks and assets of defined patients and populations. | Ask people about their access to transportation. |
| Adjustment | Activities that focus on altering clinical care to accommodate identified social barriers. | Reduce the need for in-person health care appointments by using other options such as telehealth appointments. |
| Assistance | Activities that reduce social risk by providing assistance in connecting patients with relevant social care resources. | Provide transportation vouchers so that patients can travel to health care appointments. Vouchers can be used for ride-sharing services or public transit. |
| Alignment | Activities undertaken by health care systems to understand existing social care assets in the community, organize them to facilitate synergies, and invest in and deploy them to positively affect health outcomes. | Invest in community ride-sharing or time-bank programs. |
| Advocacy | Activities in which health care organizations work with partner social care organizations to promote policies that facilitate the creation and redeployment of assets or resources to address health and social needs. | Work to promote policies that fundamentally change the transportation infrastructure within the community. |
SOURCE: NASEM, 2019.
the area of awareness, for example, clinical nurses in a hospital setting can identify the fall risks their patients might face upon discharge and the assets they can incorporate into their lives to improve their health. In the area of adjustment, telehealth and/or home health and home visiting nurses can alter clinical care to reduce the risk of falls by, for example, helping patients to adjust risks in their homes and learn to navigate their environment. And these activities can continue to the high level of system change through advocacy for health policies aimed at altering community infrastructure to help prevent falls.
In short, improving population health entails challenging and changing the factors and institutions that give rise to health inequity through interventions and reforms that influence the institutions, social systems, and public policies that drive health (Lantz, 2019). It is important to note, however, that there are shortcomings in how evaluations of health equity interventions are carried out (see Box 5-1).
ADDRESSING SOCIAL NEEDS IN CLINICAL SETTINGS
Although the provision of clinical care is a downstream determinant of health, the clinical setting presents an opportunity for nurses to address midstream determinants, or social needs, as well. Screening for social needs and making referrals to social services is becoming more commonplace in clinical settings as part of efforts to provide holistic care (Gottlieb et al., 2016; Makelarski et al., 2017; Thomas-Henkel and Schulman, 2017). Nurses may conduct screenings; review their results; create care plans based on social needs as indicated by those results; refer patients to appropriate professionals and social services; and coordinate care by interfacing with social workers, community health workers, and social services providers. Although the importance of screening people for social needs has led more providers to take on this role, it has yet to become a universal practice (CMS, 2020; NASEM, 2016), as most physician practices and hospitals do not perform screenings for the five key domains of social need1: food insecurity, housing instability, utility needs, transportation needs, and interpersonal violence (CMS, 2020; Fraze et al., 2019). As trusted professionals that spend significant time with patients and families, nurses are well equipped to conduct these screenings (AHA, 2019). Federally qualified health centers (FQHCs)—community-based health centers that receive funds from the Health Resources and Services Administration’s (HRSA’s) Health Center Program—often screen for social needs.
In many clinical settings, however, challenges arise with screening for social needs. Individuals may be hesitant to provide information about such issues as housing or food insecurity, and technology is required to collect social needs data and once obtained, to share these data across settings and incorporate them into
___________________
1 These five domains of social needs are part of the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services’ Accountable Health Communities Model (Fraze et al., 2019).
nursing practice in a meaningful way. While nurses have an educational foundation for building the skills needed to expand their role from assessing health issues to conducting assessments and incorporating findings related to social needs into care plans, this focus needs to be supported by policies where nurses are employed. As the incorporation of social needs into clinical consideration expands, nurses’ education and training will need to ensure knowledge of the impact of social needs and SDOH on individual and population health (see Chapter 7). Communicating appropriately with people about social needs can be difficult, and training is required to ensure that people feel comfortable responding to personal questions related to such issues as housing instability, domestic violence, and financial insecurity (Thomas-Henkel and Schulman, 2017). Finally, the utility of social needs screening depends on networks of agencies that offer services and resources in the community. Without the ability to connect with relevant services, screenings and care plans can have little impact. Consequently, it is important for health care organizations to dedicate resources to ensuring that people are connected to appropriate resources, and to follow up by tracking those connections and offering other options as needed (Thomas-Henkel and Schulman, 2017).
ADDRESSING SOCIAL NEEDS AND SOCIAL DETERMINANTS OF HEALTH IN THE COMMUNITY
While interest in and action to address social needs in the clinical setting is rapidly expanding, nurse engagement in these issues in community settings has been long-standing. Nurses serving in the community often work directly to address social needs at the individual and family levels, and often work as well to address SDOH at the community and population levels. Public health nurses in particular have broad knowledge of health issues and the associated SDOH, as well as needs and resources, at the community level. Embedded within the community, they also are well positioned to build trust and are respected among community leaders. Also playing important roles in addressing social needs within the community are home visiting nurses. At the individual and family levels, home visiting nurses often represent the first line of health care providers with sustained engagement in addressing social needs for many individuals. They recognize and act on the limitations associated with social needs, such as the inability to afford transportation, or may work with an interdisciplinary team at the Special Supplemental Nutrition Program for Women, Infants, and Children (WIC) clinic to address food issues and other social needs. By connecting with individuals in their neighborhoods and homes, public health and other community-based nurses promote health and well-being for families within communities and engage in this work with partners from across social, health, and other services.
At the population health level, public health nurses work to achieve health equity within communities through both health promotion and disease prevention and control. They often work in municipal and state health departments and apply
nursing, social, epidemiology, and other public health sciences in their contributions to population health (Bigbee and Issel, 2012; IOM, 2011 [see AARP, 2010]; Larsen et al., 2018). They offer a wide range of services to individuals and community members and are engaged in activities ranging from policy development and coalition building to health teaching and case management (Minnesota Department of Health, n.d.). Public health nurses serve populations that include those with complex health and social needs, frail elderly, homeless individuals, teenage mothers, and those at risk for a specific disease (Kulbok et al., 2012). Their interventions may target specific health risks, such as substance use disorder, HIV, and tobacco use, or populations at risk for health problems, such as individuals with complex health and social needs. Specific knowledge and skills they bring to communities include the ability to perform assessments of individual, family, and community health needs; use data and knowledge of environmental factors to plan for and respond to public health issues in their community; provide community and health department input in the development of policies and programs designed to improve the health of the community; implement evidence-based public health programs; and develop and manage program budgets (Minnesota Department of Health, n.d.).
Public health nursing roles are characterized by collaboration and partnerships with communities to address SDOH (Kulbok et al., 2012). Core to public health nursing is working across disciplines and sectors to advance the health of populations through community organizing, coalition building, policy analysis, involvement in local city and county meetings, collaboration with state health departments, and social marketing (Canales et al., 2018; Keller et al., 2004). Yet, while the work of public health nurses is foundational to the health of communities, their work is rarely visible. Additionally, regarding measurable reductions in health disparities, little research is available that connects directly and explicitly to public health nursing roles (Davies and Donovan, 2016; Schaffer et al., 2015; Swider et al., 2017).
Recent experiences with H1N1, Ebola, Zika, and COVID-19 underscore the importance of having strong, well-connected, well-resourced social services, public health, and health care systems, matched by an adequate supply of well-educated nurses. A 2017 report from the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine focused on global health notes that when infectious disease outbreaks occur, significant costs are often associated with fear and the worried-well seeking care (NASEM, 2017b). In their role as trusted professionals, and given their widespread presence in communities, incorporating public health nurses into community, state, and federal government strategies for health education and dissemination of information can help extend the reach and impact of messaging during infectious disease outbreaks and other public health emergencies. Nurses can serve as expert sources of information (e.g., on preventing infectious disease transmission within their communities) (Audain and Maher, 2017). In the United States, for example, as Zika infections were
identified and spreading, one of the strategies used by the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) was to work through nursing associations to reach nurses and through them, help reach the public with factual information and minimize unnecessary resource use (Minnesota Department of Health, 2019). Given their expertise in community engagement and knowledge of local and state government health and social services assets, public health nurses are well positioned to link to and share health-related information with community partners to help reach underresourced populations, including homeless individuals, non-English-speaking families, and others.
WORKING ACROSS DISCIPLINES AND SECTORS TO MEET MULTIPLE NEEDS
As nurses work in concert with other sectors and disciplines, interventions that address multiple and complex needs of individuals and communities can have far-reaching impacts on health outcomes and health care utilization. Through partnerships, community-based nurses work to address an array of health-related needs ranging from population-level diabetes management to community-based transportation to enable low-income families to access health care services.
Because multiple factors influence individual and population health, a multidisciplinary, multisectoral approach is necessary to improve health and reduce health inequity. While an approach focusing on only one SDOH may improve one dimension of health, such as food insecurity, intersectional approaches that simultaneously address complex, holistic needs of individuals, families, and communities are often required. Commonly found across underresourced communities are layers of intersecting challenges impacting health, ranging from adverse environmental exposures to food deserts. Health care systems, community-based organizations, government entitities, nurses, and others are increasingly working together to design interventions that reflect this complexity (NASEM, 2017a, 2019). Creative alliances are being built with for-profit and not-for-profit organizations, community groups, federal programs, hospitals, lending institutions, technology companies, and others (NASEM, 2019).
Work to prioritize and address health disparities and achieve health equity is predicated on meaningful, often multidimensional, assessments of community characteristics. One key opportunity to inform multisectoral efforts lies in community health needs assessments. The Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act requires nonprofit hospitals to conduct these assessments every 3 years, with input from local public health agencies. These assessments are then used to identify and prioritize significant health needs of the community served by the hospital while also identifying resources and plans for addressing these needs. Conducting a community health needs assessment is itself a multisectoral collaboration as it requires engaging community-based stakeholders (Heath, 2018). The results of the assessment present opportunities for multiple sectors to work
together. For example, a hospital may partner with public health and area food banks to address food insecurity. Or it may partner with a health technology company and a local school board to address digital literacy for underserved youth and their families, and also extend the reach of broadband to support health care access through telehealth technology and strengthen digital literacy. In assessing the community’s health needs, these hospitals are required to obtain and consider community-based input, including input from individuals or organizations with knowledge of or expertise in public health. The reports produced as part of this process are required to be publicly available (IRS, 2020).
These and other community engagement efforts can involve nurses from a variety of clinical and community-based settings in any and all steps of the process, from design to implementation and evaluation of the assessments themselves or the processes and programs established to address identified priorities. For example, the Magnet recognition program of the American Nurses Credentialing Center requires participating hospitals to involve nurses in their community health needs assessments (ANCC, 2017).
A variety of models feature nurses directly addressing health and social needs through multidisciplinary, multisectoral collaboration. Two illustrative programs are described below: the Camden Core Model and Edge Runner.
Camden Core Model
The Camden Coalition, based in Camden, New Jersey, is a multidisciplinary, nonprofit organization that works across sectors to address health and social needs. The Coalition’s formation was based on the recognition that the U.S. health care system far too often fails people with complex health and social needs. These individuals cycle repeatedly through multiple health care, social services, and other systems without realizing lasting improvements in their health or well-being. The Coalition employs multiple approaches that include using faith-based partnerships to deliver health services and encourage healthy choices; sharing data among the criminal justice, health care, and housing sectors to identify points of intervention; and building local and national coalitions to support and educate others interested in implementing this model (Camden Coalition, n.d.). One of the Coalition’s best-known programs is the Camden Core Model. This nationally recognized care management intervention is an example of a nurse-led care management program for people with complex medical and social needs. It applies the principles of trauma-informed care and harm reduction with the aim of empowering people with the skills and support they need to avoid preventable hospital use and improve their well-being (Finkelstein et al., 2020; Gawande, 2011). The model uses real-time data on hospital admissions to identify “superutilizers,” people with complex health issues who frequently use emergency care. An interprofessional team of registered nurses (RNs) and licensed practical nurses (LPNs), social workers, and community health workers engage in person
with these individuals to help them navigate their care by connecting them with medical care, government benefits, and social services (Camden Coalition, n.d.; Finkelstein et al., 2020). With federal funding, similar versions of the model have been extended to cities outside of Camden (AF4Q, 2012; Crippen and Isasi, 2013; Mann, 2013).
Camden Coalition partnerships optimize the use of nurses in the community in several ways. An interprofessional team of nurses, social workers, and community health workers visits program participants, helps reconcile their medications, accompanies them to medical visits, and links them to social and legal services. Critical to the model’s success is recruiting nurses who are from the local community, capitalizing on their cultural and systems-level knowledge to facilitate and improve access to and utilization of local health and social services. The culture of the Camden Coalition model has been key to its success. The uniform commitment of nurses, staff, and leadership to addressing people’s complex needs has created a supportive work environment in which each team member’s role is optimized. Care Team members have accompanied people to their meetings and appointments for primary care, helped with applications for such public benefits as food stamps, provided referrals to social services and housing agencies, arranged for medication delivery in partnership with local pharmacies, and coordinated care among providers.
The Camden Coalition focuses on “authentic healing relationships,” defined as secure, genuine, and continuous partnerships between Care Team members and patients. This emphasis has evolved into a framework for patient engagement known as COACH, which stands for Connect tasks with vision and priorities, Observe the normal routine, Assume a coaching style, Create a backward plan, and Highlight progress with data. An interprofessional team of nurses, social workers, and community health workers visits participants in the community. Team members are trained to problem solve with patients to achieve the program goals of helping them manage their chronic health conditions and reducing preventable hospital admissions.
Early evidence of the program’s effect in a small sample showed a 56 percent reduction in monthly hospital charges, a roughly 40 percent reduction in monthly visits to hospitals and emergency departments, and an approximately 52 percent increase in rates of reimbursement to care providers (Green et al., 2010), although later evidence from a randomized controlled trial (RCT) indicated that the Camden Core Model did not reduce hospital readmissions (Finkelstein et al., 2020). Other RCTs, conducted in Philadelphia and Chicago, showed that similar social care programs using case management and community health workers can reduce hospital admissions and save money in addition to improving health and quality of health care. Kangovi and colleagues (2018) conducted an RCT in Philadelphia to assess Individualized Management for Patient-Centered Targets (IMPaCT), a standardized community health worker intervention addressing unmet social needs across three health systems (Kangovi et al., 2018). After 6 months, patients
in the intervention group compared with controls were more likely to report the highest quality of care and spent fewer total days in the hospital (reduced by about two-thirds), saving $2.47 for each dollar invested by Medicaid annually (Kangovi et al., 2020). The RCT in Chicago assessed the effectiveness of a case management and housing program in reducing use of urgent medical services among homeless adults with chronic medical conditions and found a 29 percent reduction in hospitalizations and a 24 percent reduction in emergency department visits (Sadowski et al., 2009).
Edge Runner
The American Academy of Nurses’ Edge Runner initiative identifies and promotes nurse-designed models of care and interventions that can improve health, increase health care access and quality, and/or reduce costs (AAN, n.d.a). As of February 2020, 59 such programs had been evaluated against a set of criteria and designated as part of this initiative. Many Edge Runner programs are built around the needs of underserved communities and seek to improve health through holistic care that addresses social needs and SDOH, including a range of upstream, midstream, and downstream determinants. Mason and colleagues (2015) assessed 30 Edge Runner models identified as of 2012, finding four main commonalities that illustrate these programs’ broad and encompassing approach to health.
A holistic definition of health. Across the programs, health was defined broadly to include physical, psychological, social, spiritual, functional, quality-of-life, personal happiness, and well-being aspects. Additionally, the definition of health was based on the values of clients and shaped around their preferences. Typically, programs were grounded in SDOH to inform their design of individual- and community-level interventions.
Individual-, family-, and community-centric design. Most programs prioritized individual, family, and community goals over provider-defined goals through a “participant-led care environment” and “meeting people where they are.” Thus, interventions were tailored to the values and culture present at each of these three levels.
Relationship-based care. The programs reflected the importance of building trusting relationships with individuals, families, and communities to help them engage in ways to create and sustain their own health.
Ongoing group and public health approaches to improving the health of underserved populations. The nurses who designed the programs viewed serving underserved populations as a moral imperative. Through peer-to-peer education, support groups, and public health approaches, they sought to empower clients, give them a sense of control, build self-care agency, and increase resilience.
An in-depth study of three Edge Runner programs (the Centering Pregnancy model, INSIGHTS, and the Family Practice and Counseling Network) revealed particular lessons: the essential role of collaboration and leaders who can col-
laborate with a wide range of stakeholders, the need for plans for scalability and financial sustainability, and the importance of social support and empowerment to help people (Martsolf et al., 2017). In these and other models, the capacity and knowledge associated with building meaningful, sustained partnerships across sectors is a key dimension of nursing practice that impacts health equity. The Edge Runner programs emphasize how, in the pursuit of improving care, lowering costs, and increasing satisfaction for people and families, nurses are actively working to achieve person-centered care that addresses social needs and SDOH and focusing on the needs of underserved populations to promote health equity (Martsolf et al., 2016, 2017; Mason et al., 2015). However, evidence directly linking the programs to decreases in disparities is generally not available. Two examples of Edge Runner programs are described in Box 5-2.
As models continue to evolve and be disseminated, it is critical to establish an evidence base that can help understand their impact on health and well-being and their contribution to achieving the broader aim of health equity. For care management programs incorporating social care, it is important to consider a broad array of both quantitative and qualitative measures beyond health care utilization (Noonan, 2020). Although RCTs generate the most reliable evidence, this evidence can be limited in scope. For example, the RCTs cited above assessed neither the multidimensional nature of care management/social care models that might be reflected in such outcomes as client self-efficacy, satisfaction, or long-term health outcomes nor their potential social impacts. Also important to note is that care management models incorporating social care are limited by the availability of resources in the community, such as behavioral health services, addiction treatment, housing, and transportation. Programs that connect clients to health and social
services are unlikely to work if relevant services are unavailable (Noonan, 2020). Important to underscore in the context of this report is that multisector engagement, as well as health care teams that may involve social workers, community health workers, physicians, and others engaging alongside nurses, all are oriented to a shared agenda focused on improving health and advancing health equity.
ADVOCATING FOR POLICY CHANGE
Public policies have a major influence on health care providers, systems, and the populations they serve. Accordingly, nurses can help promote health equity by bringing a health lens to bear on public policies and decision making at the community, state, and federal levels. Informing health-related public policy can involve communicating about health disparities and SDOH with the public, policy makers, and organizational leaders, focusing on both challenges and solutions for addressing health through actions targeted to achieving health equity.
When nurses engage with policy change as an upstream determinant of health, they can have a powerful and far-reaching impact on the health of populations. In the National Academy of Medicine’s Vital Directions series, Nancy Adler and colleagues (2016) note that “powerful drivers of health lie outside the conventional medical care delivery system…. Health policies need to expand to address factors outside the medical system that promote or damage health.” Because health inequities and SDOH are based in social structures and policies, efforts to address them upstream as the root of poor health among certain populations and communities need to focus on policy change (NASEM, 2017a). Nurses alone cannot solve the problems associated with upstream SDOH that exist outside of health care systems. However, by engaging in efforts aimed at changing local, state, or federal policy with a Health in All Policies approach,2 they can address SDOH that underlie poor health (IOM, 2011; NASEM, 2017a; Williams et al., 2018). Whether nurses engage in policy making full time or work to inform policy part time as a professional responsibility, their attention to policies that either create or eliminate health inequities can improve the underlying conditions that frame people’s health. Nurses can bring a health and social justice lens to public policies and decision making at the community, state, and federal levels most effectively by serving in public- and private-sector leadership positions. Much of this work is discussed in Chapter 9 on nursing leadership, but it is noted in this chapter given the substantial
___________________
2 Health in All Policies (HiAP) is a collaborative approach that integrates health considerations into policy making across sectors. It recognizes that health is created by a multitude of factors beyond health care and in many cases, beyond the scope of traditional public health activities. In accordance with HiAP, for example, decision makers in the health care sector should consider transportation, education, housing, commerce, and other sectors impacting communities. HiAP stresses the need to work across government agencies and with private partners from these different sectors to achieve healthy and safe communities. It also encourages partnerships between the health care sector and community developers, for example (CDC, 2016).
influence that policy decisions have on health equity. Nurses can and should use their expertise to promote policies that support health equity.
For example, a nurse in Delaware was influential in getting the state’s legislature to pass legislation to implement a colorectal cancer screening program that has increased access to care and reduced disparities in morbidity and mortality from colorectal cancer (see Box 5-3). While individual nurses, often through their workplace and professional associations, engage in upstream efforts to impact health equity, there have been repeated calls from within the nursing community for more nurses to engage in informing public policy to improve health outcomes for individuals and populations.
CONCLUSIONS
In the coming decade, the United States will make substantial progress in achieving health equity only if it devotes resources and attention to addressing the adverse effects of SDOH on the health of underresourced populations. As 2030 approaches, numerous initiatives to address health equity are likely to be launched at the local, state, and national levels. Many of these initiatives will focus on health care equity. Yet, while expanding access to quality care is critical to reducing disparities and improving health outcomes, such efforts need to be accompanied by additional efforts to identify and change the social institutions, dynamics, and systems underlying health inequities from the local to the national level. Nurses can contribute to reshaping the landscape of health equity over the coming decade by serving in expanded roles, working in new settings and new ways, and partnering with communities and other sectors beyond health care. Some nurses are already working in roles and settings that support health equity and are engaged in educating about and advocating for health equity through their professional associations. Nonetheless, broader engagement as a core activity of every nurse will help advance health equity nationwide. To achieve this aim will require
- support for and the willingness of the nursing workforce to take on new roles in new settings in the community;
- consistency in nurses’ preparation for engaging in downstream, midstream, and upstream strategies aimed at improving health equity by addressing issues that compromise health, such as geographic disparities, poverty, racism, homelessness, trauma, drug abuse, and behavioral health conditions;
- more experiential learning and opportunities to work in community settings throughout nursing education to ensure that nurses have skills and competencies to address individuals’ complex needs and promote efforts to improve the well-being of communities;
- nursing education that goes beyond teaching the principles of diversity, equity, and inclusion to provide sustained student engagement in hands-on community and clinical experiences with these issues;
- funding to support new models of care and functions that address SDOH, health equity, and population health; and
- evaluation of models to build the evidence needed to scale programs and the policies and resources necessary to sustain them.
These issues are discussed in the chapters that follow. Programs described in this chapter, such as the Camden Coalition and the Edge Runner initiatives, are exemplars of the kind of multidisciplinary, multisector efforts that will be necessary to address the complex needs of individuals and communities and make a lasting impact by eliminating health disparities, with the goal of achieving health equity. Central to these future efforts, however, are parallel efforts that evaluate
and provide the evidence base on which to determine the effectiveness of models. One of the greatest challenges this committee faced was finding evidence directly linking the efforts of nurses to address social needs and SDOH to reductions in health disparities that would signal improved population health outcomes and health equity. Such evidence is essential to informing payment policy decisions that can ensure the sustainability of and nurse engagement in these models (discussed further in Chapter 6). Through evidence, the nursing profession can leverage its own potential, and the public, other professionals, and other sectors can understand the impact and value of such nursing engagement.
Conclusion 5-1: Nurses are in a position to improve outcomes for the underserved and can work to address the structural and institutional factors that produce health disparities in the first place.
Conclusion 5-2: Nurses can use their unique expertise and perspective to help develop and advocate for policies and programs that promote health equity.
REFERENCES
AAN (American Academy of Nursing). n.d.a. Transforming America’s health system through nursing solutions. https://www.aannet.org/initiatives/edge-runners (accessed November 3, 2020).
AAN. n.d.b. ¡Cuídate!: A culturally-based program to reduce sexual risk behavior among Latino youth. https://www.aannet.org/initiatives/edge-runners/profiles/edge-runners--cuidate (accessed November 3, 2020).
AAN. n.d.c. Insights into children’s temperament: Supporting the development of low-income children. https://www.aannet.org/initiatives/edge-runners/profiles/edge-runners--insights-into-childrens-temperament (accessed November 3, 2020).
AARP. 2010. Preparation and roles of nursing care providers in America. http://championnursing.org/resources/preparation-and-roles-nursing-care-providers-america (accessed June 3, 2021).
Abellanoza, A., N. Provenzano-Hass, and R. J. Gatchel. 2018. Burnout in ER nurses: Review of the literature and interview themes. Journal of Applied Biobehavioral Research 23(1):e12117.
Adler, N. E., M. M. Glymour, and J. Fielding. 2016. Addressing social determinants of health and health inequalities. Journal of the American Medical Association 316(16):1641–1642.
AF4Q (Aligning Forces for Quality). 2012. Expanding “hot spotting” to new communities. http://forces4quality.org/node/5182.html (accessed November 3, 2020).
Agurs-Collins, T., S. Persky, E. D. Paskett, S. L. Barkin, H. I. Meissner, T. R. Nansel, S. S. Arteaga, X. Zhang, R. Das, and T. Farhat. 2019. Designing and assessing multilevel interventions to improve minority health and reduce health disparities. American Journal of Public Health 109(S1):S86–S93.
AHA (American Hospital Association). 2019. Screening for social needs: Guiding care teams to engage patients. Chicago, IL: American Hospital Association.
ANA (American Nurses Association). 2020. ANA president condemns racism, brutality and senseless violence against black communities. https://www.nursingworld.org/news/news-releases/2020/ana-president-condemns-racism-brutality-and-senseless-violence-against-black-communities (accessed September 17, 2020).
ANCC (American Nurses Credentialing Center). 2017. 2019 Magnet® application manual. Silver Spring, MD: American Nurses Credentialing Center.
Audain, G., and C. Maher. 2017. Prevention and control of worldwide mosquito-borne illnesses: Nurses as teachers. Online Journal of Issues in Nursing 22(1):5.
Bigbee, J. L., and L. M. Issel. 2012. Conceptual models for population-focused public health nursing interventions and outcomes: The state of the art. Public Health Nursing 29(4):370–379.
Braveman, P., E. Arkin, T. Orleans, D. Proctor, and A. Plough. 2017. What is health equity? And what difference does a definition make? Princeton, NJ: Robert Wood Johnson Foundation.
Bridge, J. A., L. Asti, L. M. Horowitz, J. B. Greenhouse, C. A. Fontanella, A. H. Sheftall, K. J. Kelleher, and J. V. Campo. 2015. Suicide trends among elementary school–aged children in the United States from 1993 to 2012. JAMA Pediatrics 169(7):673–677.
Brown, A. F., G. X. Ma, J. Miranda, E. Eng, D. Castille, T. Brockie, P. Jones, C. O. Airhihenbuwa, T. Farhat, L. Zhu, and C. Trinh-Shevrin. 2019. Structural interventions to reduce and eliminate health disparities. American Journal of Public Health 109(S1):S72–S78.
Camden Coalition. n.d. Camden core model. https://camdenhealth.org/care-interventions/camden-core-model (accessed November 4, 2020).
Canales, M. K., D. J. Drevdahl, and S. M. Kneipp. 2018. Letter to the editor: Public health nursing. Nursing Outlook 66(2):110–111.
Castrucci, B., and J. Auerbach. 2019. Meeting individual social needs falls short of addressing social determinants of health. Health Affairs Blog. doi: 10.1377/hblog20190115.234942.
CDC (Centers for Disease Control and Prevention). 2016. Health in all policies. https://www.cdc.gov/policy/hiap/index.html (accessed June 2, 2021).
CMS (Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services). 2020. Z codes utilization among Medicare fee-for-service (FFS) beneficiaries in 2017. Baltimore, MD: Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services Office of Minority Health.
Crippen, D., and F. Isasi. 2013. The untold story of 2013: Governors lead in health care transformation. Health Affairs Blog. https://www.healthaffairs.org/do/10.1377/hblog20131217.035878/full (accessed June 2, 2021).
Davies, N., and H. Donovan. 2016. National survey of commissioners’ and service planners’ views of public health nursing in the UK. Public Health 141:218–221.
Donley, R., and M. J. Flaherty. 2002. Revisiting the American Nurses Association’s first position on education for nurses. Online Journal of Issues in Nursing 7(2):2.
Duran, D., Y. Asada, J. Millum, and M. Gezmu. 2019. Harmonizing health disparities measurement. American Journal of Public Health 109(S1):S25–S27.
Dye, B. A., D. G. Duran, D. M. Murray, J. W. Creswell, P. Richard, T. Farhat, N. Breen, and M. M. Engelgau. 2019. The importance of evaluating health disparities research. American Journal of Public Health 109(S1):S34–S40.
Finkelstein, A., A. Zhou, S. Taubman, and J. Doyle. 2020. Health care hotspotting—A randomized, controlled trial. New England Journal of Medicine 382(2):152–162.
Fraze, T. K., A. L. Brewster, V. A. Lewis, L. B. Beidler, G. F. Murray, and C. H. Colla. 2019. Prevalence of screening for food insecurity, housing instability, utility needs, transportation needs, and interpersonal violence by us physician practices and hospitals. JAMA Network Open 2(9):e1911514.
Gawande, A. 2011 (January 24). The hot spotters. https://www.newyorker.com/magazine/2011/01/24/the-hot-spotters (accessed October 14, 2020).
Gottlieb, L. M., D. Hessler, D. Long, E. Laves, A. R. Burns, A. Amaya, P. Sweeney, C. Schudel, and N. E. Adler. 2016. Effects of social needs screening and in-person service navigation on child health: A randomized clinical trial. JAMA Pediatrics 170(11):e162521.
Green, S. R., V. Singh, and W. O’Byrne. 2010. Hope for New Jersey’s city hospitals: The Camden initiative. Perspectives in Health Information Management 7(Spring):1d.
Grubbs, S. S., B. N. Polite, J. Carney, Jr., W. Bowser, J. Rogers, N. Katurakes, P. Hess, and E. D. Paskett. 2013. Eliminating racial disparities in colorectal cancer in the real world: It took a village. Journal of Clinical Oncology 31(16):1928–1930.
Healthy Delaware. 2020. Welcome Consortium Members and Partners. https://www.healthydelaware.org/Consortium (accessed November 3, 2020).
Heath, S. 2018. 3 things to know to conduct a community health needs assessment. https://patientengagementhit.com/news/3-things-to-know-to-conduct-a-community-health-needs-assessment (accessed October 6, 2020).
IOM (Institute of Medicine). 2011. The future of nursing: Leading change, advancing health. Washington, DC: The National Academies Press.
IRS (Internal Revenue Service). 2020. Community health needs assessment for charitable hospital organizations-Section 501(r)(3). https://www.irs.gov/charities-non-profits/community-health-needs-assessment-for-charitable-hospital-organizations-section-501r3 (accessed June 2, 2021).
Jones, N. L., N. Breen, R. Das, T. Farhat, and R. Palmer. 2019. Cross-cutting themes to advance the science of minority health and health disparities. American Journal of Public Health 109(S1):S21–S24.
Kangovi, S., N. Mitra, L. Norton, R. Harte, X. Zhao, T. Carter, D. Grande, and J. A. Long. 2018. Effect of community health worker support on clinical outcomes of low-income patients across primary care facilities: A randomized clinical trial. JAMA Internal Medicine 178(12):1635–1643.
Kangovi, S., N. Mitra, D. Grande, J. Long, and D. Asch. 2020. Evidence-based community health worker program addresses unmet social needs and generates positive return on investment. Health Affairs 39(2). doi: 10.1377/hlthaff.2019.00981.
Keller, L. O., S. Strohschein, M. A. Schaffer, and B. Lia-Hoagberg. 2004. Population-based public health interventions: Innovations in practice, teaching, and management. Part II. Public Health Nursing 21(5):469–487.
Krist, A. H., T. A. Wolff, D. E. Jonas, R. P. Harris, M. L. LeFevre, A. R. Kemper, C. M. Mangione, C.-W. Tseng, and D. C. Grossman. 2018. Update on the methods of the U.S. Preventive Services task force: Methods for understanding certainty and net benefit when making recommendations. American Journal of Preventive Medicine 54(1 Suppl 1):S11–S18.
Kulbok, P. A., E. Thatcher, E. Park, and P. S. Meszaros. 2012. Evolving public health nursing roles: Focus on community participatory health promotion and prevention. Online Journal of Issues in Nursing 17(2):1.
Lantz, P. M. 2019. The medicalization of population health: Who will stay upstream? Milbank Quarterly 97(1):36–39.
Larsen, R., J. Ashley, T. Ellens, R. Frauendienst, K. Jorgensen-Royce, and M. Zelenak. 2018. Development of a new graduate public health nurse residency program using the core competencies of public health nursing. Public Health Nursing 35(6):606–612.
Makelarski, J. A., E. Abramsohn, J. H. Benjamin, S. Du, and S. T. Lindau. 2017. Diagnostic accuracy of two food insecurity screeners recommended for use in health care settings. American Journal of Public Health 107(11):1812–1817.
Mann, C. 2013. CMCS informational bulletin: Targeting Medicaid super-utilizers to decrease costs and improve quality. Baltimore, MD: Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services.
Martsolf, G. R., T. Gordon, L. Warren May, D. Mason, C. Sullivan, and A. Villarruel. 2016. Innovative nursing care models and culture of health: Early evidence. Nursing Outlook 64(4):367–376.
Martsolf, G. R., D. J. Mason, J. Sloan, C. G. Sullivan, and A. M. Villarruel. 2017. Nurse-designed care models: What can they tell us about advancing a culture of health? Santa Monica, CA: RAND Corporation.
Mason, D. J., D. A. Jones, C. Roy, C. G. Sullivan, and L. J. Wood. 2015. Commonalities of nurse-designed models of health care. Nursing Outlook 63(5):540–553.
Minnesota Department of Health. 2019. Public health interventions: Applications for public health nursing practice, 2nd ed. St. Paul, MN: Minnesota Department of Health.
Minnesota Department of Health. n.d. Public health nurse orientation and resource guide. https://www.health.state.mn.us/communities/practice/ta/phnconsultants/guide-phn.html (accessed October 5, 2020).
Mullan, F. 2017. Social mission in health professions education: Beyond flexner. Journal of the American Medical Association 318(2):122–123.
NASEM (National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine). 2016. Accounting for social risk factors in Medicare payment: Identifying social risk factors. Washington, DC: The National Academies Press.
NASEM. 2017a. Communities in action: Pathways to health equity. Washington, DC: The National Academies Press.
NASEM. 2017b. Global health and the future role of the United States. Washington, DC: The National Academies Press.
NASEM. 2019. Integrating social care into the delivery of health care: Moving upstream to improve the nation’s health. Washington, DC: The National Academies Press.
Noonan, K. 2020. Disappointing randomized controlled trial results show a way forward on complex care in Camden and beyond. Health Affairs Blog. doi: 10.1377/hblog20200102.864819.
Pittman, P. 2019. Rising to the challenge: Re-embracing the Wald model of nursing. American Journal of Nursing 119(7):46–52.
Rafferty, A. M. 2015 (January 27). Reinventing nursing’s social mission. Video. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=8PjoiO8v-dE (accessed September 6, 2020).
Sadowski, L. S., R. A. Kee, T. J. VanderWeele, and D. Buchanan. 2009. Effect of a housing and case management program on emergency department visits and hospitalizations among chronically ill homeless adults: A randomized trial. Journal of the American Medical Association 301(17):1771–1778.
Schaffer, M. A., L. O. Keller, and D. Reckinger. 2015. Public health nursing activities: Visible or invisible? Public Health Nursing 32(6):711–720.
Swider, S. M., P. F. Levin, and V. Reising. 2017. Evidence of public health nursing effectiveness: A realist review. Public Health Nursing 34(4):324–334.
Thomas-Henkel, C., and M. Schulman. 2017. Screening for social determinants of health in populations with complex needs: Implementation considerations. Trenton, NJ: Center for Health Care Strategies.
Tyson, T., C. J. Kenon, Jr., and K. Nance. 2018. Nursing at historically black colleges and universities. Journal of Professional Nursing 34(3):167–170.
Williams, D. R., and V. Purdie-Vaughns. 2016. Needed interventions to reduce racial/ethnic disparities in health. Journal of Health Politics, Policy and Law 41(4):627–651.
Williams, S. D., J. M. Phillips, and K. Koyama. 2018. Nurse advocacy: Adopting a health in all policies approach. Online Journal of Issues in Nursing 23(3).
Woolf, S. H., J. Q. Purnell, S. M. Simon, E. B. Zimmerman, G. J. Camberos, A. Haley, and R. P. Fields. 2015. Translating evidence into population health improvement: Strategies and barriers. Annual Review of Public Health 36(1):463–482.
This page intentionally left blank.




















