2
Implications for the National Agenda on Fostering the Healthy Mental, Emotional, and Behavioral Development of Youth
The National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine has convened multiple committees in recent years focusing on the healthy mental, emotional, and behavioral development of children and adolescents. Representatives from three reports shared some of those key findings with the workshop audience. Claire Brindis, codirector of the Adolescent and Young Adult Health National Resource Center at the University of California in San Francisco presented the 2019 National Academies consensus study report on The Promise of Adolescence: Realizing Opportunity for All Youth (NASEM, 2019b). Nicole Kahn, program officer at the National Academies, gave an overview of the 2020 National Academies consensus study report, Promoting Positive Adolescent Health Behaviors and Outcomes: Thriving in the 21st Century (NASEM, 2020). Tamar Mendelson, director of the Center for Adolescent Health at the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health, then presented the 2019 National Academies report Fostering Healthy Mental, Emotional, and Behavioral Development in Children and Youth (NASEM, 2019a). This chapter provides background contextualization on the charge and recommendations of each report and concludes with a discussion facilitated by Stephanie Jones, professor of education at the Harvard Graduate School of Education.
PROMISE OF ADOLESCENCE
Brindis began by introducing participants to the National Academies 2019 report on The Promise of Adolescence: Realizing Opportunity for
All Youth.1 The study was tasked with providing an evidence-based report examining the following:
- Neurobiological and socio-behavioral characteristics in adolescent development and the influences this period exerts on development trajectories.
- The shaping of adolescent development by early life conditions pertaining to both support and adversity.
- Revelations by science about our ability during the adolescent period to mediate the past developmental challenges of many youth and children.
- Structural inequalities and their ability to promote or threaten adolescent development.
- Historical trauma and its role in health development.
- Suggested ways for changing systems of wealth, health, justice, and child welfare to improve the process and outcomes of adolescent development.
- Ways that systems can recognize and support the formation of resilience, while promoting adolescent agency and the development of positive assets.
Inequity and Adolescence
The study committee placed a thematic focus on the effects of inequity on adolescent development. Brindis stated that inequality in opportunity and access can severely curtail the promise of adolescence for many youths, and that it is important to not only consider individual behavior but also the influence structural inequalities and societal determinants exert on life-course trajectories. Overall, the committee recognized the reality that “adolescence is a period of extraordinary opportunity for learning and exploration and for laying a strong foundation for a successful life” and the need for our nation “to commit itself to a sustained plan for reversing the worsening inequities of childhood disadvantage, thereby enabling all adolescents to flourish,” Brindis said.
Interplay between Biology and Environmental Epigenetics
Brindis elaborated on why the report highlighted the need for focusing on adolescent development specifically, and the influence that epigenetics and the environmental pressures that shape individuals exerts on the way
___________________
1 The full list of recommendations from this report is provided in Appendix D.
heredity is expressed. The trajectory of an individual’s life can be altered depending on the protective factors present at each stage. She defined protective factors within the environment as supportive relationships, access to resources, nutrition, place of residence, quality of air, social interactions, and lifestyle choices. These protective factors are shaped by social determinants such as education, employment, health systems and services, quality of housing, income, access to resources, public safety, physical environment, and social environment. As Figure 2-1 shows, an individual’s trajectory can be positively or negatively shaped by various environmental influences. The presence or absence of protective factors can be the difference in a developmental outcome being positive or negative.
In congruence with the epigenetic approach, Brindis explained, the life-course perspective analyzes demographic and social changes by implying that an individual’s current circumstances are a result of prior life experiences and circumstances. The epigenetic approach embraces a trajectory model of the life-course perspective and emphasizes the role of brain plasticity in how trajectories in brain circuits and body systems can be positively or negatively influenced depending on the environment.
Areas of Opportunity for Reform
The sensitive yet malleable period of adolescent development presents unique opportunities to influence neurobiological behavior and life trajectories. Brindis stated that because adolescents experience increased curiosity and reward sensitivity, societal incentives should encourage them to embrace longer-term rewards. The increase in cognitive abilities during this developmental period provides a capacity for psycho-social developmental tasks such as developing identity and capacity for self-direction, said Brindis. Furthermore, the adolescent brain’s malleability coupled with the adolescent’s active role in their own development create timely opportunities for programs that promote beneficial changes in developmental trajectories for youth with a history of adverse experiences. Brindis argued that it is time to reimagine and redesign the systems and settings that adolescents most frequently encounter. To do this, researchers might adopt a philosophy that emphasizes the importance of the adolescent developmental period and its implications on life-course trajectories, she said. She highlighted potential changes and opportunities for redesigning education, health, child welfare, and justice systems. These are summarized briefly below.
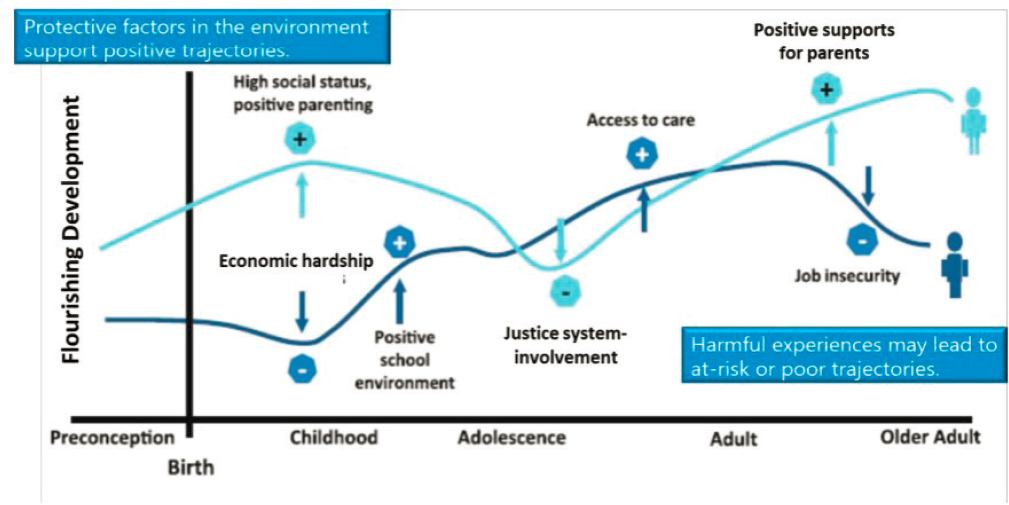
SOURCE: The Promise of Adolescence: Realizing Opportunity for All Youth, Figure 3-2. Adapted from Halfon, N., Larson, K., Lu, M., Tullis, E., and Russ, S. (2014).
Education System2
Elaborating on areas of opportunity, Brindis focused on the impact of education in young people’s lives. She invited participants to reflect on the needs of young people in imagining a future education system. A key aspect for future consideration is precision education that is differentiated and responsive to academic opportunities. Precision education includes individualized instruction, tutoring, and credentialing. Additionally, Brindis said, we could also consider what nonacademic skills can be incorporated such as decision making, practical knowledge, and adaptability, all of which constitute a successful education.
Health System3
Moving on to opportunities in the health system, Brindis stressed the importance of access to appropriate health care services. Access to health care can affect adolescents’ well-being not only in the present but throughout their lifetime as they develop habits that will impact both their health and our country’s health status, she explained. Financial barriers are associated with limited access to health care, which can contribute to longstanding disparities. Additional health system challenges that adolescents face include inexperience in navigating the complex health care system, confidentiality concerns regarding their care, and an increase in the likelihood of engaging in risky behaviors.
To address these challenges, Brindis suggested developmentally appropriate changes to provider practices and innovative care models to help adolescents become more engaged in their own care. As an example, she proposed that health systems could offer integrated, comprehensive services that prepare youth for the physical, cognitive, and social changes that take place during adolescence. This process would also include the integration of behavioral health, substance-abuse prevention, and physical health services. Furthermore, she highlighted the importance of teaching adolescents to navigate the health system so that they will be able to successfully do so as adults. Brindis also emphasized the importance of providing services that are culturally informed and able to respond to geographic, economic, sexual preference, financial, ethnic, and racial differences.
___________________
2 See https://www.nap.edu/read/25388/chapter/10 for more information.
Child Welfare System4
Next, Brindis addressed the child welfare system, which presents a unique set of challenges for a particularly vulnerable population. Brindis recognized the progress that Congress has made over the past 20 years, but said that attention is still needed to evaluate what resources are required to accomplish family reunification and prioritize placement with relatives over strangers, as well as what resources are available for children aging out of the foster-care system. At the same time, Brindis said, additional efforts will be required to go beyond the existing progress to address adoption at the state level of some optional federal laws. By doing so, she added, all adolescents associated with the child welfare system will have the opportunity to flourish.
Justice System5
Finally, the juvenile justice system presents a wide array of opportunities for improvement. These include increased family engagement and greater attention to procedural fairness in terms of such things as interactions with police, legal representation options, and reduced use of juvenile fines and fees. Brindis stated that reforms in these areas within the criminal justice system take into account the differences in the developmental needs of older adolescents and young adults. For instance, she said, attention should be given to reducing the frequency of automatic transfers of juveniles to criminal courts based only on the charged offense, as well as to the creation of developmentally informed correctional programs for young offenders. Brindis acknowledged the work being done in communities across the country such as youth courts and commended the communities trying to find alternatives to incarceration during these vulnerable developmental periods.
Moving Forward
Closing her presentation, Brindis emphasized the collective responsibility of society to build systems that support and promote positive adolescent development, and she said that these systems work best when they reflect the specific socio-ecological circumstances of each child. Brindis argued that systems should recognize adolescence as a significant period of learning and discovery and use it to remediate past developmental challenges. “As
___________________
a society, we must harness the promise of adolescence so that all youth can thrive,” she stated.
PROMOTING POSITIVE ADOLESCENT HEALTH BEHAVIORS AND OUTCOMES
Nicole Kahn, study director of the related National Academies Committee on Applying Lessons of Optimal Adolescent Health to Improve Behavioral Outcomes for Youth, presented the committee’s 2020 report Promoting Positive Adolescent Health Behaviors and Outcomes: Thriving in the 21st Century.6 The committee was tasked with reviewing key questions related to the effective implementation of the national Teen Pregnancy Prevention (TPP) program and exploring the existing scientific literature surrounding core components of adolescent health programs using an optimal health lens. Kahn defined these core components as the “active ingredients” of an intervention. Identifying core components allows program directors to focus on the parts of a program that work, which can then be organized in ways to achieve intended results. In addition to these charges, the committee was also tasked with recommending the following:
- A research agenda that incorporated a focus on optimal health for youth.
- Ways in which the Office of the Assistant Secretary for Health (OASH) at the Department of Health and Human Services could use its role to encourage the adoption of promising elements of youth-focused programs and initiatives such as mental and physical health care, adolescent development science, and reproductive health and teen pregnancy care.
- Improvements for OASH youth-focused programs.
Committee Findings
Kahn described the main takeaways from the committee’s findings. First, healthy risk taking in adolescence is not only normal but necessary. Instead of conceptualizing all risk taking as negative, Kahn asserted that acknowledging the developmental purposes of risk taking, as well as encouraging and providing opportunities for healthy risks, is beneficial. In addition to this, Kahn also said it is important to help youth discern between healthy and unhealthy risks. Healthy risk environments and opportunities allow youth to explore their environments, practice decision making, and cultivate independence. Examples of healthy risk taking include trying new
___________________
6 The full list of recommendations from this report is provided in Appendix E.
foods, asking someone out on a date, or trying out for a team sport. Unhealthy risks are things such as driving under the influence, bullying, and having unprotected sex, all things that can have harmful effects on development and result in negative outcomes.
The second key finding from the report was that more research is needed to identify, measure, and evaluate the effective components of adolescent health behavior programs. She said that while the committee did find research that identifies the most common core components of programs, more research is needed to specify which components are most effective. By doing so, shorter and more focused programs can be created which would make them less costly, require less training, and increase their accessibility to diverse populations.
The third key takeaway of the report is that socio-emotional learning and positive youth development programs provide a foundation upon which other specific skills and services such as understanding social norms around drugs and contraceptive access can be built, Kahn continued. These socio-emotional learning and positive youth development programs are responsible for providing critical building-block skills like self-regulation, good decision making, social awareness, and relationship skills, all of which are necessary for youth when learning to discern between healthy and unhealthy risks.
The fourth main finding of the report, Kahn said, is that all programs can benefit from implementing and evaluating policies and practices that promote inclusiveness and equity. Examples of this include the incorporation of diverse cultures and lifestyles and the expansion of the existing cultural resources of families and communities. Merely having policies and practices in place are not enough, Kahn argued, and actions must be taken to ensure that programs are formally measured and evaluated as adolescent behavior programs continue to develop.
The final message of the report, Kahn stated, is that since youth are experts in their own lives and active participants in their own development, it makes sense to involve them in the decision making that affects them.
Kahn closed her presentation with a quote from the 2019 public information gathering session by Natnael Abate, peer educator with Promising Future DC:
And for me, what I think is a thriving person in 2019 is when you’re physically, mentally, and emotionally stable. I feel like you accept yourself for who you are, and you’re around people that support you emotionally, and you can in return give that support back.
Kahn viewed Abate’s insight as a call to action to facilitate environments to ensure that youth can thrive in multiple domains of their lives.
NATIONAL AGENDA ON FOSTERING THE HEALTHY MENTAL, EMOTIONAL, AND BEHAVIORAL DEVELOPMENT OF YOUTH
Tamar Mendelson, who served as a committee member for the National Academies 2019 report Fostering Healthy Mental, Emotional, and Behavioral Development in Children and Youth, presented the committee’s statement of task, which was to compose a consensus study on fostering mental, emotional, and behavioral (MEB) health in young people. The committee was specifically requested to review key research, strategy advances, and challenges since the release of the 2009 report Preventing Mental, Emotional, and Behavioral Disorders Among Young People: Progress and Possibilities. They were also asked to report on recent progress in understanding what is needed for effective implementation strategies as well as to identify program, policy, and research gaps for promoting healthy MEB development. In addition to these charges, the committee was to take the following into consideration: prevalence trends of specific MEB conditions, the current context for health promotion strategies using a public health framework, biological and environmental influences, two-generation approaches, and the use of complementary and integrative approaches such as mindfulness.
Committee Findings
Mendelson presented the 2019 report as an amplification of two previous National Academies reports: the 2009 report Preventing Mental, Emotional, and Behavioral Disorders Among Young People: Progress and Possibilities, which itself was an update to the 1994 report Reducing Risk for Mental Disorders. The 2019 report included an expanded version of the mental health intervention spectrum originally published in the 1994 report. As Figure 2-2 shows, the 2019 committee added a promotion sector previously not included. Mendelson explained that this new section is included to highlight promotion throughout the various levels of intervention: individual and family, community, and societal.
In considering this spectrum, the committee recommended an expansion of the range of interventions to develop, evaluate, and implement, as well as an increased emphasis on promotion. Mendelson pointed out that while advances in prevention have been made since the 2009 report, the high prevalence of mental disorders is still unacceptable. Many still wait to seek help because of the stigma surrounding mental illness and lack of access to evidence-based care. Mendelson explained that an emphasis on implementation science was also made in the 2019 report with the purpose of increasing the integration of effective strategies into systems of care in the real world.
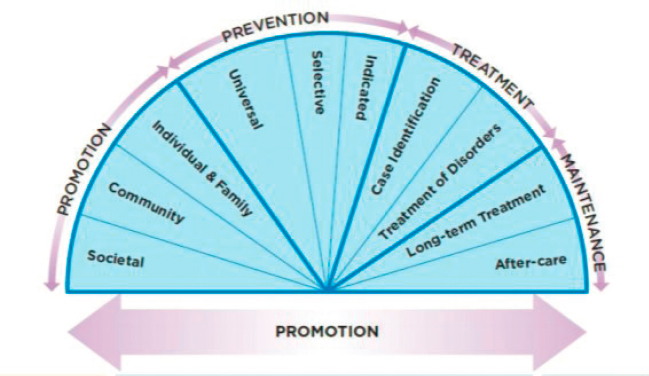
SOURCE: NASEM, 2019a, Figure 1-3.
Life Course Perspective Model
Echoing the findings of The Promise of Adolescence: Realizing Opportunity for all Youth, Mendelson explained how the committee utilized the life-course perspective model to identify possible interventions. Committee members focused on preconception through young adulthood and identified interventions that would have the most optimal developmental effects at each stage of life. The committee, Mendelson explained, felt strongly that focusing solely or primarily on the individual interventions would have a weaker effect on prevalence than was needed. They instead placed an emphasis on community interventions and social policy that would yield more effective community-level and population-level effects.
Environmental Impact: Epigenetics
The report included a dynamic figure explaining the impact of epigenetics on mental health development (see Figure 2-3). Described previously by Brindis as an influential factor in their report, Mendelson noted that this committee explored the complex neurobiological processes that interact with the physical and social environment, which unfolds from the point of preconception through adolescence and also intergenerationally. She explained the various ways in which environments shape neurodevelopment, such as the influential effects of experiences that affect conception, gestation, and childbirth, characteristics of the family and community, and characteristics of the broader society.
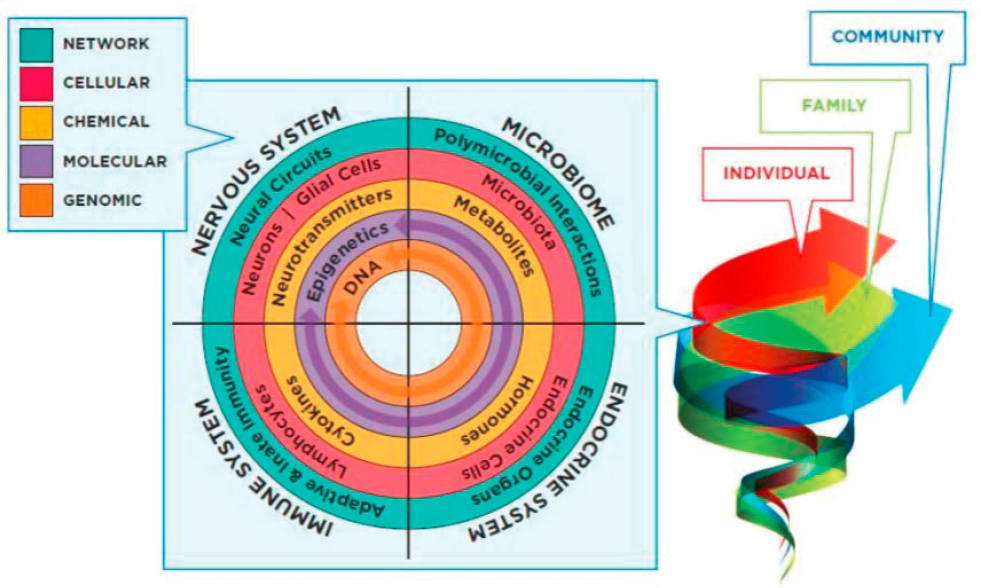
SOURCE: NASEM, 2019a, Figure 2-2.
Implementation Process
Mendelson emphasized the report’s focus on the implementation of programs and policies as a key contributor to effectiveness on a population scale. Identifying core components is a necessary step for the effectiveness of long-term outcomes. In addition to this, she said, adapting programs and policies for diverse settings as well as establishing an ongoing interactive implementation system are equally important. An interactive implementation system might include active engagement with community partners such as community coalitions, a well-trained workforce, active leadership and management, continuous fidelity monitoring feedback to maintain focus, a quality and outcomes monitoring system, evaluation-based learning, and multiple methods of communication with stakeholders.
Effective Intervention Strategies
Based on the ways child development is affected, the report committee included strategies for effective intervention implementation on the generational, educational, health care, community, and policy levels. The committee recommended improvements regarding generational interventions, as well as evaluation methods to measure the impacts of these interventions on offspring. Mendelson emphasized the importance of leveraging the education system for intervention strategies to yield positive health outcomes that can last for years. Primary care settings within health care are also opportune for promoting MEB health, and Mendelson encouraged the audience to consider ways in which MEB health strategies can be effectively integrated into health care. She went on to highlight the importance and benefit of strategies at the community level, saying that living in communities with access to social, economic, and physical resources that promote health and well-being increase the opportunity to thrive. Regarding policy-level strategies, Mendelson stated that while the evidence base regarding the use of local, state, and federal policies to promote MEB health is growing, it is incomplete.
Recommendations from the Report Committee
The report included a list of recommendations regarding state and local level coordination, policy level improvement, funding, and data monitoring, as seen in Box 2-1.
The report also included a specific set of research recommendations, which Mendelson listed:
- Design an evaluation of scalable interventions at the population level.
- Design, evaluate, and implement effective school-based interventions.
- Develop successful two-generation interventions in health care.
- Design policy strategies to address effects of social, racial, and economic disparities on MEB health.
- Design and evaluate implementation strategies.
The recommendations align with the committee’s vision, which Mendelson described as a holistic approach to MEB health and development. This involves stakeholders recognizing the importance of measuring and tracking health and development, community empowerment, public health campaigns raising awareness for program improvement, health care providers and educators working for improvements, businesses investing in the well-being of employees, and governments considering MEB data in policy decisions.
DISCUSSION
Stephanie Jones summarized the overlapping themes of this discussion, saying that there was much continuity across reports. “We’ve heard about utilizing a life-course perspective with a focus on adolescence, the interplay of risk and protective systems integrated with biology, the essential role of promotion efforts combined with prevention and intervention efforts, and a call for more focus on implementation innovations and scaling of interventions,” she said. Jones also asked the speakers what they thought the next steps would be for reframing the dialogue around adolescence. Brindis pro-
posed that a reframing of the stereotype of adolescents is needed to recognize the potential of adolescents in development. This prompted a question from a participant, who asked how momentum could be gained from the information presented and leveraged into national policy. Kahn responded by highlighting the key relationships that the National Academies have with the federal government, and that this has allowed committee findings to be relayed to officials on the national level. Brindis also added that she believes improvements can be made in effectively translating the existing evidence and highlighting effective policies already implemented across the country to be used as models for national policy. Mendelson echoed support for the points made by both Brindis and Kahn and also stressed the importance of including young people in the process to improve MEB health.














